
To store data locally in order to speed up subsequent retrievals. Reserved areas of memory in every computer that are used to speed up instruction execution, data retrieval and data updating. Pronounced "cash," they serve as staging areas, and their contents are constantly changing. There are two kinds: memory caches and disk caches.
File Compression
 Encoding data to take up less storage space and less bandwidth for transmission. Digital data are compressed by finding repeatable patterns of binary 0s and 1s. The more patterns can be found, the more the data can be compressed. Text can typically be compressed to approximately 40% of its original size, and graphics files from 20% to 90%. Some files compress very little. It depends entirely on the type of file and compression algorithm used.
Encoding data to take up less storage space and less bandwidth for transmission. Digital data are compressed by finding repeatable patterns of binary 0s and 1s. The more patterns can be found, the more the data can be compressed. Text can typically be compressed to approximately 40% of its original size, and graphics files from 20% to 90%. Some files compress very little. It depends entirely on the type of file and compression algorithm used.File Decompression
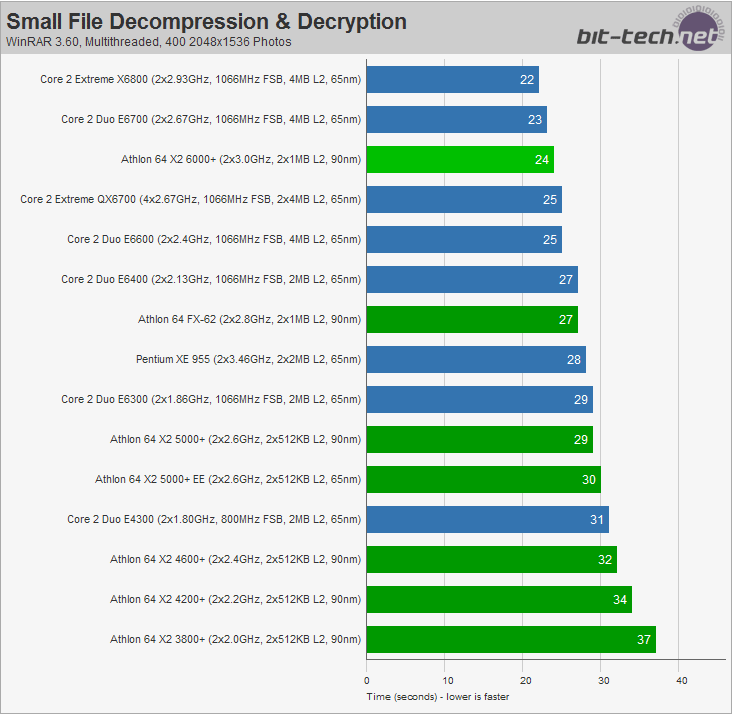 Data compression is the encoding of data to consume less space and bandwidth. Data decompression is the reverse--the decoding of compressed data to restore the original data. Compression/decompression algorithms look for redundancies in data, then minimize them using predetermined algorithms (methods). There are different algorithms used to achieve different compression rates.
Data compression is the encoding of data to consume less space and bandwidth. Data decompression is the reverse--the decoding of compressed data to restore the original data. Compression/decompression algorithms look for redundancies in data, then minimize them using predetermined algorithms (methods). There are different algorithms used to achieve different compression rates.Internet Hard Drive
 The sole purpose of an Internet hard drive is to offer a means of accessing your computer files (pictures, documents, music, videos, etc.) from any computer, as long as that computer has access to the Internet. Similar to depositing money into your bank account, and later withdrawing that same money from any ATM machine, an Internet hard drive will allow you to "deposit" your computer files into a remote hard drive, and then later access those very same files from any other computer.
The sole purpose of an Internet hard drive is to offer a means of accessing your computer files (pictures, documents, music, videos, etc.) from any computer, as long as that computer has access to the Internet. Similar to depositing money into your bank account, and later withdrawing that same money from any ATM machine, an Internet hard drive will allow you to "deposit" your computer files into a remote hard drive, and then later access those very same files from any other computer.Optical Disk Drive
 A direct access storage device that is written and read by light. The most common optical discs in use are CDs and DVDs, and they come in three types: read-only, write-once and rewritable. CD, CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, DVD-Video as well as BD-ROM (Blu-ray) are read-only discs that are recorded at the time of manufacture and cannot be erased. CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R, BD-R, WORM and magneto-optic (in WORM mode) discs are write-once. They are recorded in the user's environment, but cannot be erased. CD-RW, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, BD-RE and MO discs are rewritable.
A direct access storage device that is written and read by light. The most common optical discs in use are CDs and DVDs, and they come in three types: read-only, write-once and rewritable. CD, CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, DVD-Video as well as BD-ROM (Blu-ray) are read-only discs that are recorded at the time of manufacture and cannot be erased. CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R, BD-R, WORM and magneto-optic (in WORM mode) discs are write-once. They are recorded in the user's environment, but cannot be erased. CD-RW, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, BD-RE and MO discs are rewritable.Solid-state Storage

Non mechanical. Solid state refers to electronic circuits composed of transistors, resistors, capacitors and other components, which may be discrete, single devices, or millions of them can be created in a single chip. For example, microprocessors and memories are all solid state. In a solid state device, there is no mechanical action, although an unbelievable amount of electromagnetic action takes place within.
A computer has solid state and non-solid state parts. The solid state components are the motherboard, chips, screen, camera and optical mouse, while the hard drive, CD/DVD drive, fans, keyboard, microphone, speakers and mechanical mouse are both electronic and mechanical and thus not solid state.
No comments:
Post a Comment