
The common method of interacting with a computer that allows any graphics image to be displayed on screen. Except for entering text on the keyboard, the primary way the computer is operated is with a mouse or touchpad pointing device. The mouse/touchpad is used to select icons and menu options as well as move and resize windows that frame the application and elements within it. The major GUIs are Windows and Mac along with GNOME and KDE for Linux.
Word processor
The creation of text documents. Except for labels and envelopes, it has replaced the electric typewriter in most offices, because of the ease in which documents can be edited, searched and reprinted.
Advanced word processors function as elementary desktop publishing systems. Although there are still machines dedicated only to word processing, most word processing is performed on general-purpose computers using word processing software such as Microsoft Word and WordPerfect.
Spreadsheet
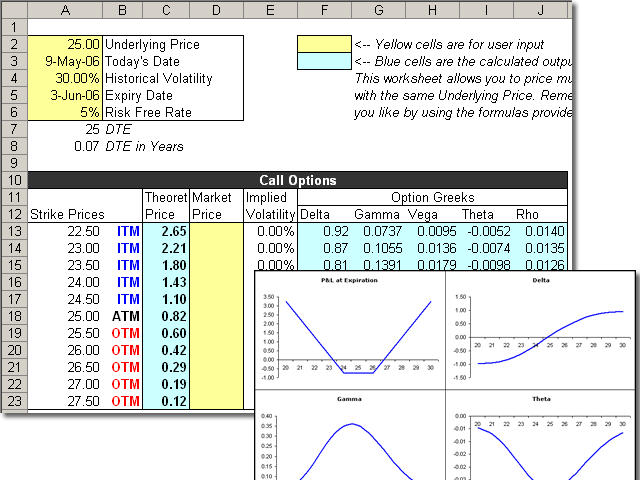
Software that simulates a paper spreadsheet (worksheet), in which columns of numbers are summed for budgets and plans. It appears on screen as a matrix of rows and columns, the intersections of which are called "cells." The cells are filled with (1) labels, (2) numeric values or (3) formulas.
Labels are descriptive text such as "Rent" and "Gross Sales." Values are the actual numeric data, and formulas command the spreadsheet to do the calculations; for example, SUM CELLS A5 TO A10.
DBMS

(DataBase Management System) Software that controls the organization, storage, retrieval, security and integrity of data in a database. It accepts requests from the application and instructs the operating system to transfer the appropriate data. The major DBMS vendors are Oracle, IBM, Microsoft and Sybase (see Oracle database, DB2, SQL Server and ASE). MySQL is a very popular open source product (see MySQL).
DBMSs let information systems be changed more easily as the organization's requirements change. New categories of data can be added to the database without disruption to the existing system. Adding a field to a record does not require changing any of the programs that do not use the data in that new field.
Utility suites
is a kind of system software designed to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer which allows users to do things like creating text documents, playing games, listening to music or surfing the web. Due to this focus, utilities are often rather technical and targeted at people with an advanced level of computer knowledge.
Web authoring

A category of software that enables the user to develop a Web site in a desktop publishing format. The software will generate the required HTML coding for the layout of the Web pages based on what the user designs. Typically, the user can toggle back and forth between the graphical design and the HTML code and make changes to the Web page in either the design of the accompanying code.
To design and create a Web site, from writing the site's underlying code to writing the text to managing the site's upkeep.
Audio editing software


A digital audio editor is a computer application for audio editing, i.e. manipulating digital audio. Digital audio editors are the main software component of a digital audio workstation.
Bitmap image

bitmap or pixmap is a type of memory organization or image file format used to store digital images. The term bitmap comes from the computer programming terminology, meaning just a map of bits, a spatially mapped array of bits. Now, along with pixmap, it commonly refers to the similar concept of a spatially mapped array of pixels. Raster images in general may be referred to as bitmaps or pixmaps, whether synthetic or photographic, in files or memory.
In certain contexts, the term bitmap implies one bit per pixel, while pixmap is used for images with multiple bits per pixel
Desktop publishing program

system for producing printed materials that consists of a personal computer personal computer (PC), small but powerful computer primarily used in an office or home without the need to be connected to a larger computer. PCs evolved after the development of the microprocessor made possible the hobby-computer movement of the late 1970s, when or computer workstation, a high-resolution printer printer, computer output device that reproduces data on paper or another medium. Impact printers use a mechanical hammering device to produce each character.
(usually a laser printer), and a computer program computer program, a series of instructions that a computer can interpret and execute; programs are also called software to distinguish them from hardware, the physical equipment used in data processing that allows the user to select from a variety of type fonts and sizes, column justifications, page layouts, and graphics libraries and often includes support for document creation and editing. Desktop publishing enables a small business or an individual to produce professional-quality materials on the premises inexpensively and quickly without the need for outside typesetting or printing facilities.
HTML editor

A low-level Web site authoring tool that is essentially a text editor, specialized for writing HTML code. It assists the HTML author by cataloging all HTML tags and common structures in menus and by being able to catch certain syntax errors. It often displays tags and contents in colors so they pop out for easy reference.
Image editor

Software that allows images to be edited and also converted to different graphics formats. Image editors typically deal with only bitmapped images such as GIFs, JPEGs and BMPs; however, some editors support both bitmaps and illustrations. Common functions are manually cropping and resizing the image and using "filters" to adjust brightness, contrast and colors. A myriad of filters are available for special effects. Red eye removal is included in editors specialized for photos.
Multimedia

As the name implies, multimedia is the integration of multiple forms of media. This includes text, graphics, audio, video, etc. For example, a presentation involving audio and video clips would be considered a "multimedia presentation." Educational software that involves animations, sound, and text is called "multimedia software." CDs and DVDs are often considered to be "multimedia formats" since they can store a lot of data and most forms of multimedia require a lot of disk space.
Vector image

Unlike JPEGs, GIFs, and BMP images, vector graphics are not made up of a grid of pixels. Instead, vector graphics are comprised of paths, which are defined by a start and end point, along with other points, curves, and angles along the way. A path can be a line, a square, a triangle, or a curvy shape. These paths can be used to create simple drawings or complex diagrams. Paths are even used to define the characters of specific typefaces.
Because vector-based images are not made up of a specific number of dots, they can be scaled to a larger size and not lose any image quality. If you blow up a raster graphic, it will look blocky, or "pixelated." When you blow up a vector graphic, the edges of each object within the graphic stay smooth and clean. This makes vector graphics ideal for logos, which can be small enough to appear on a business card, but can also be scaled to fill a billboard. Common types of vector graphics include Adobe Illustrator, Macromedia Freehand, and EPS files. Many Flash animations also use vector graphics, since they scale better and typically take up less space than bitmap images.
No comments:
Post a Comment